What is beta-glucan? Aureobasidium (black yeast)
The Amazing Power of beta-glucan
What is β-glucan, which supports immune function?
Beta-glucan is a polysaccharide, a member of the dietary fiber family known to be good for the stomach.
It is found in mushrooms such as Ganoderma lucidum and Agaricus, which are also used in Chinese medicine, as well as in seaweed, barley, β-glucan is attracting attention and research in the United States and other leading health countries as an ingredient and supplement for regulating the immune system and immune balance.
Types of beta-glucan
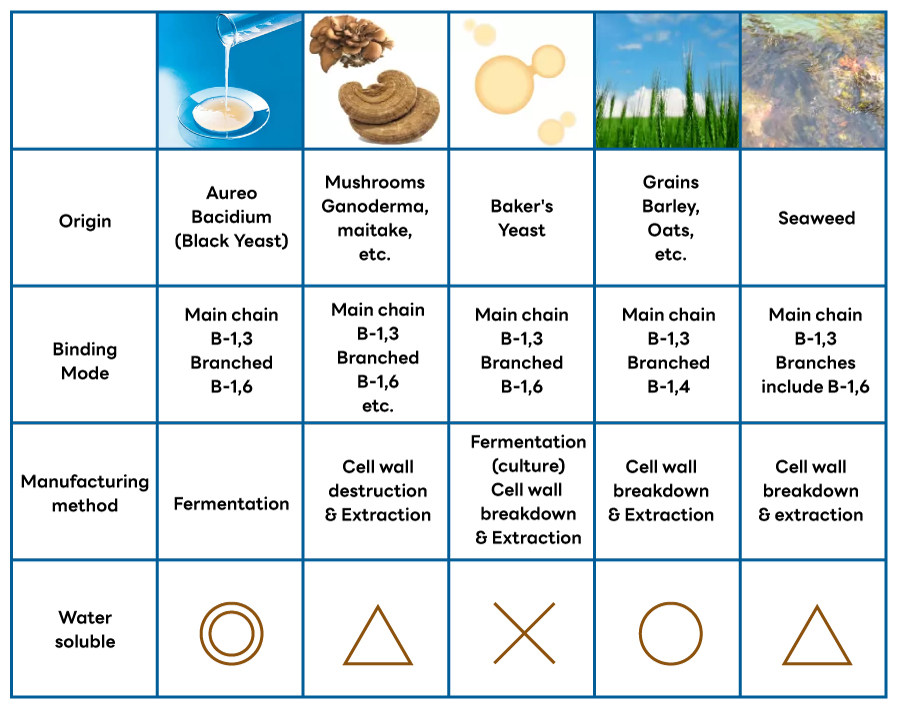
Let’s take a look at whether beta-glucan has the same efficacy.
black yeast
Black yeast is a type of microorganism that exists in nature and produces β-glucan outside the fungus by itself during fermentation.
Aureo cultivates black yeast under special conditions based on its own biotechnology, so the only modification is heat treatment. Unlike baker’s yeast-derived products, Aureo does not destroy cells or perform chemical processing such as extraction and purification, allowing the intake of β-glucan in its natural state.
The black yeast fungus is water soluble, which means that the β-glucan dissolves easily in water, and it also contains minerals and vitamin C, so it works gently on the body.
Mushrooms
Ganoderma lucidum, also used in Chinese herbal medicine, has long been prized as a “herb of longevity” with no side effects, especially the Ganoderma lucidum that grows on plum trees. recognized that the β-glucan contained in the dietary fiber of Reishi mushroom enhances human immunity, and since then, over the past 20 years, three types of Reishi mushrooms have been approved as pharmaceutical products: “Crestin” extracted from the Kawaratake mushroom, “Lentinan” extracted from the Shiitake mushroom, and “Schizophilan These three types of mushrooms have been approved as pharmaceuticals. However, it is difficult to consume β-glucan contained in mushrooms as it is,and it must be extracted or purified. In addition, β-glucan extracted from mushrooms such as maitake and agaricus is a standard health foods,but it is difficult to dissolve in water, and it is very expensive to take supplements on a daily basis.
Baker’s Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae)
In the West, where bread is a common food culture, it has been widely used as a health supplement because it has been familiar for a long time. Extraction
and purification are still necessary to produce β-glucan in the cells of the baker’s yeast fungus Another characteristic of baker’s yeast is that most commercialized baker’s yeast is a powdered dried product that is insoluble in water (not compatible with water) when ingested in capsules.
Grains
Barley contains a lot of β-glucan in the cell walls of the endosperm, and unlike white rice, β-glucan is not easily lost when barley is milled. It is also rich in protein, calcium, minerals, and vitamins, making it
a Popular health food.
Seaweeds
Kelp is rich in laminaran, a polysaccharide linked mainly by β1,3-linkages, which is said to moisturize the skin and dissolve blood clots in blood vessels.
Characteristics of Aureobasidium (black yeast) beta-glucan

In the early 1950s, a trace amount of a gelatinous substance was accidentally found in raw sugar derived from sugarcane during the production process of a certain soft drink. family produced by black yeast. After further research on cultivation methods, we succeeded in producing “Aureobasidium culture fluid,” which contained more than 10 times the β-glucan content of agaricus, which was very popular at the time, and Aureobasidium (black yeast ) β-glucan was born. The Aureobasidium (black yeast) β-glucan supplement series
was developed in order to make this excellent Aureobasidium (black yeast) β-glucan widely known throughout the world.
Gel-like substance is gentle to the body and easy to drink
When Aureobasidium (black yeast) is cultured under special conditions based on our unique biotechnology, Aureobasidium (black yeast) produces a gel-like substance, which is why Aureo’s β-glucan is gel-like with lots of water .
1,3-1 ,6 β-glucan, which is gentle to the body and can be safely consumed by both the elderly and children without catching in the throat or being aspirated
. Functionality as a material for cosmetics.
Fermented food produced from Aureobasidium (black yeast) β-glucan
Aureo supplements are a fermented food made from naturally occurring yeast called Aureobasidium (black yeast). It is a soluble dietary fiber that contains plenty of water, so it can be taken as is or added to dishes such as curry or cooking rice, as it is resistant to heat and can be used in daily menus.
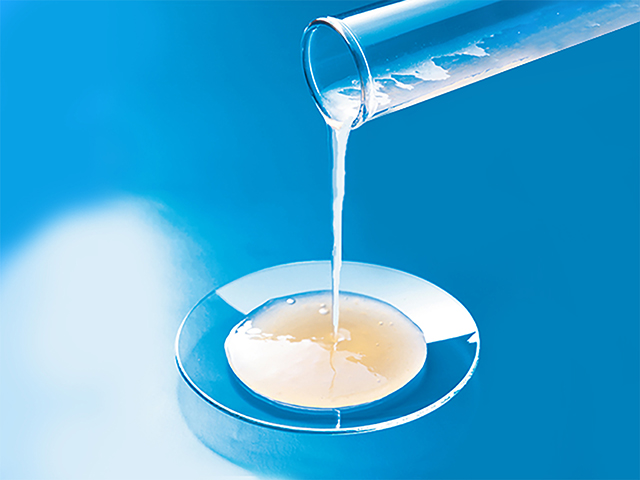
Structure of Aureobasidium (black yeast) beta-glucan
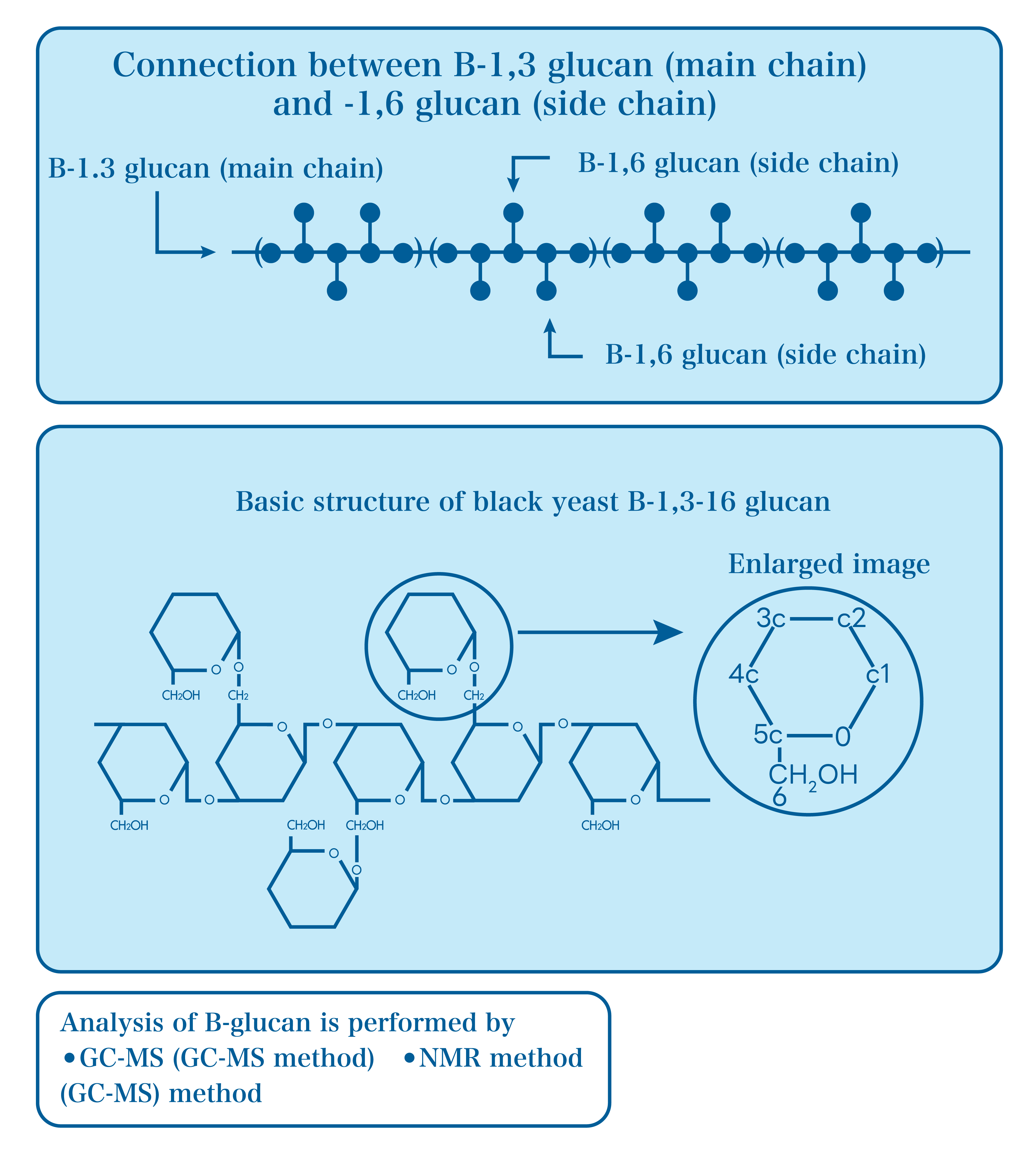
Beta-glucan is a type of polysaccharide consisting of many glucose linkages.
The smallest unit of sugar is called monosaccharide if it consists of a single sugar, disaccharide if it is a combination of two monosaccharides, and polysaccharide if more than 10 monosaccharides are connected.
Typical examples include glucose and fructose as monosaccharides, sucrose (commonly called sugar) and oligosaccharides as disaccharides, and glucan and dextrin as polysaccharides.
Glucans are also divided into alpha-glucans and beta-glucans, depending on how the glucose is linked. black yeast ) β-glucan has a β-type connection.
It has a special structure in which the trunk (main chain) has many branches (side chains).
Beta-1,3-1,6 glucan is attracting attention worldwide!
β-glucan has long been studied around the world, including at Harvard University, where receptors that can recognize β-glucan have been discovered on the surface of immune cells. It is known that when β-glucan binds to these receptors, immune cells
are Subsequent
studies have shown that β-1,3-1,6 binding is more active.
Three Reasons to Choose Aureo’s Beta Glucan Supplement

There are a wide variety of β-glucan supplements available in a variety of base ingredients, but we would like to introduce why Aureo’s β-glucan supplements have been loved and chosen for 23 years.
1. Delivering high-quality β-glucan
Health foods play a role in supporting health by being taken daily. Aureo manufactures high-quality, highly concentrated β-glucan under strict hygiene and quality control at its own factory in Japan (GMP certified) so that everyone can take it every day with peace of mind.
All products at the plant undergo quality control inspections to ensure a stable supply of products.
▶️ for more information on manufacturing and quality control
2. Top class in the industry! 23 years of trust!
Loved for 23 years. Aureo has been researching, developing, and manufacturing Aureobasidium (black yeast) β-glucan for 23 years.
We will continue to grow so that we can deliver our products to as many people as possible who desire good health.
▶️ for more information about our company.
3. Evidence based on solid research data
We conduct daily research on β-glucan in cooperation with universities and research institutions through our research divisions “Sapporo Bioscience Division” and “AureoScience Corporation,” which have offices in Hokkaido University. Evidence for health food is based on the premise that it is
safe for anyone to eat at any time and in any quantity. Aureo’s β-glucan has been patented not only in Japan, but also in Europe, the United States, and other countries where supplements are advanced, with 51 cases of rich evidence.
▶️ for more information on research and patents.
Aureobasidium Culture Solution” as an existing food additive (natural food additive)
The Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW) allows the use of food additives only when they have been evaluated for safety by the Food Safety Commission and do not pose a risk to human health, and only after setting standards for ingredients and their use Aureobasidium culture medium was officially notified as “Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (now Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare) Notification No. 120” on April 16, 1996.
The reliability of Aureobasidium culture medium was also confirmed by the Ministry of Health , Labor and Welfare in its “Research Study on the Review of Safety of Existing Additives” in June 2004.
Description of Aureobasidium culture medium
The essence and properties of the safe and reliable Aureobasidium culture medium.
Existing additive list number (1)
-
Name of product
-
Aureobasidium culture broth (from Aureobasidium culture broth, mainly composed of β-1,3-1,6 glucan)
Abbreviated or classified name
-
Fame
- Aureobasidium cultured solution
-
Basis, method, and essence
- Black yeast (Aureobasidium pullulans) culture medium.
The main component is beta-1,3-1,6 glucan.
-
Use
- thickening and stabilizing agent
-
Summary
- A viscous liquid obtained by reducing the culture of Aureobasidium fungi (Japanese name: black yeast). The main component, β-1,3-1,6 glucan, is a polysaccharide with β-1,3 glucan as the main chain, to which β-1,6 side chains and functional groups are attached, and is known to exhibit immune activation properties. This polysaccharide is contained in mushrooms and their extracts and has been attracting attention as a health food in recent years, and we have made it possible to efficiently produce it by cultivating microorganisms.
-
characteristics
- Yellow liquid
-
quality characteristics
- Viscous, heat, acid, and salt resistant. It has a slight, distinctive taste, aroma, and acidity. In addition to its use as a thickening agent, it can be expected to mask unpleasant tastes and have health benefits.
-
mellow
- Easily soluble in water.
-
Precautions for use
- Refrigerated after opening
-
Storage Precautions
- Store in a cool or dark place or refrigerated.
-
Main target foods
- Drinking water, sauces, bread, Japanese and Western confectioneries, bean paste, chilled confectioneries, processed meat products, processed fish products, noodles, soaked vegetables, jams, baked confectioneries, rice cakes, soft candies, film-type foods, seasonings, etc. . .
-
remarks
- *This table is excerpted from “Annotations to the List of Existing Food Additives” published by the Japan Food Additives Association in 1999. It lists 489 “food additives made from natural ingredients” approved by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (currently Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare) of Health, Labor and Welfare) of Health, Labor and Welfare) of Health, Labor and Welfare) of Health, Labor and Welfare) of Health, Labor and Welfare) of Health, Labor and Welfare) of Health of Health, Labor and Welfare) ), with detailed information on their essence, properties and uses.

